agricultural startups USA
On this remarkable occasion, we take the opportunity to delve into the thought-provoking theme surrounding agricultural startups USA. Let’s dive into valuable insights and offer new perspectives.
Video about agricultural startups USA
Feeding the Future: A Look at the U.S.’s Thriving Agricultural Startup Scene

The U.S. agricultural landscape is undergoing a transformative period, driven by innovative startups tackling age-old challenges with cutting-edge technology. From precision farming to sustainable practices, these entrepreneurs are reimagining how we grow, harvest, and distribute food, aiming to create a more efficient, equitable, and environmentally responsible food system. This article delves into the vibrant world of U.S. agricultural startups, exploring their diverse solutions and the potential they hold for shaping the future of food.
Tech-Driven Transformation:
At the heart of this revolution lies technology. Startups are leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, robotics, and sensor networks to optimize every stage of the agricultural process.
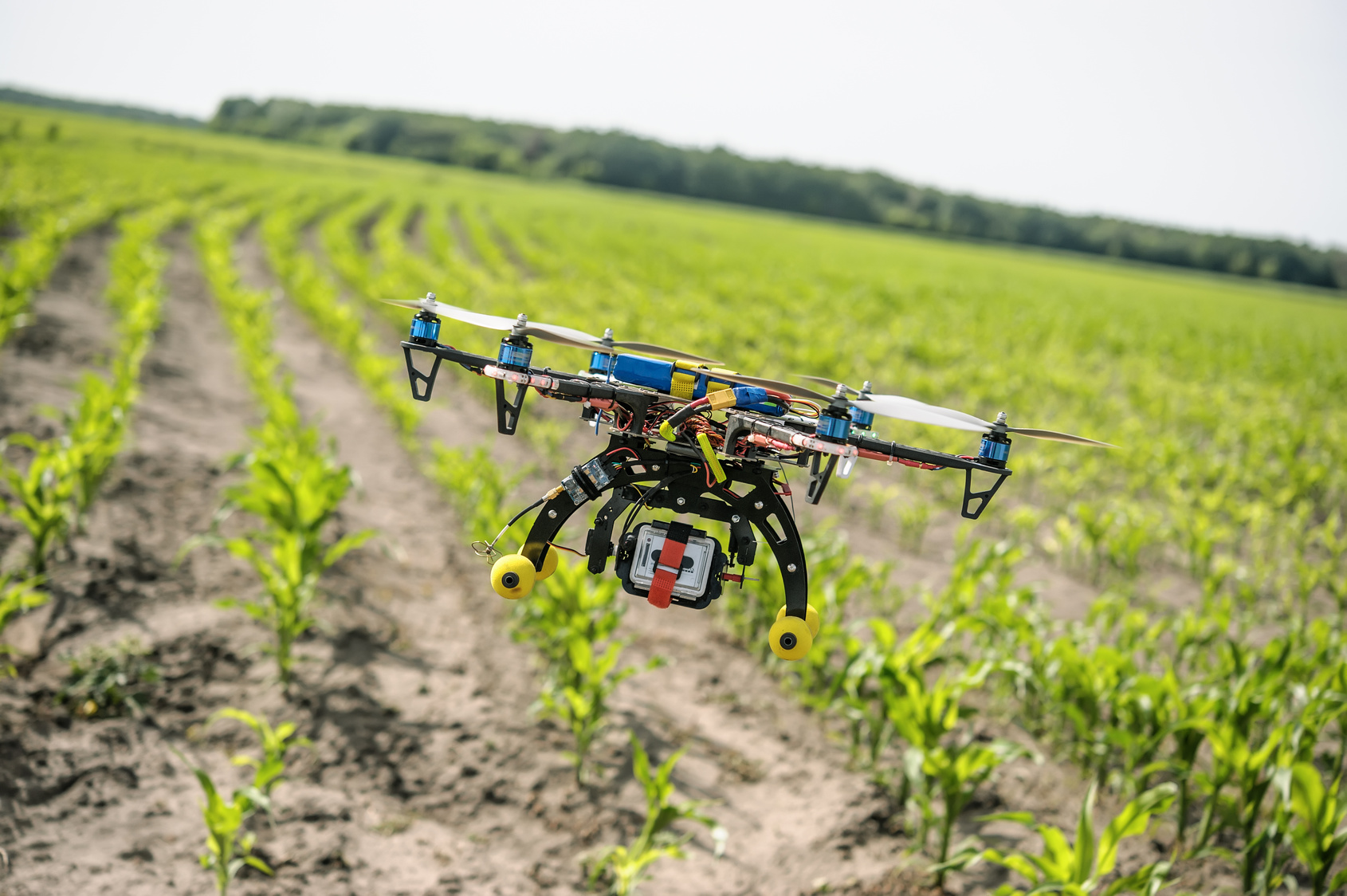
- Precision Farming: Companies like John Deere, Agribotix, and Granular are using drones, satellites, and soil sensors to collect vast amounts of data about crops, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This information allows farmers to apply fertilizers and pesticides with pinpoint accuracy, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
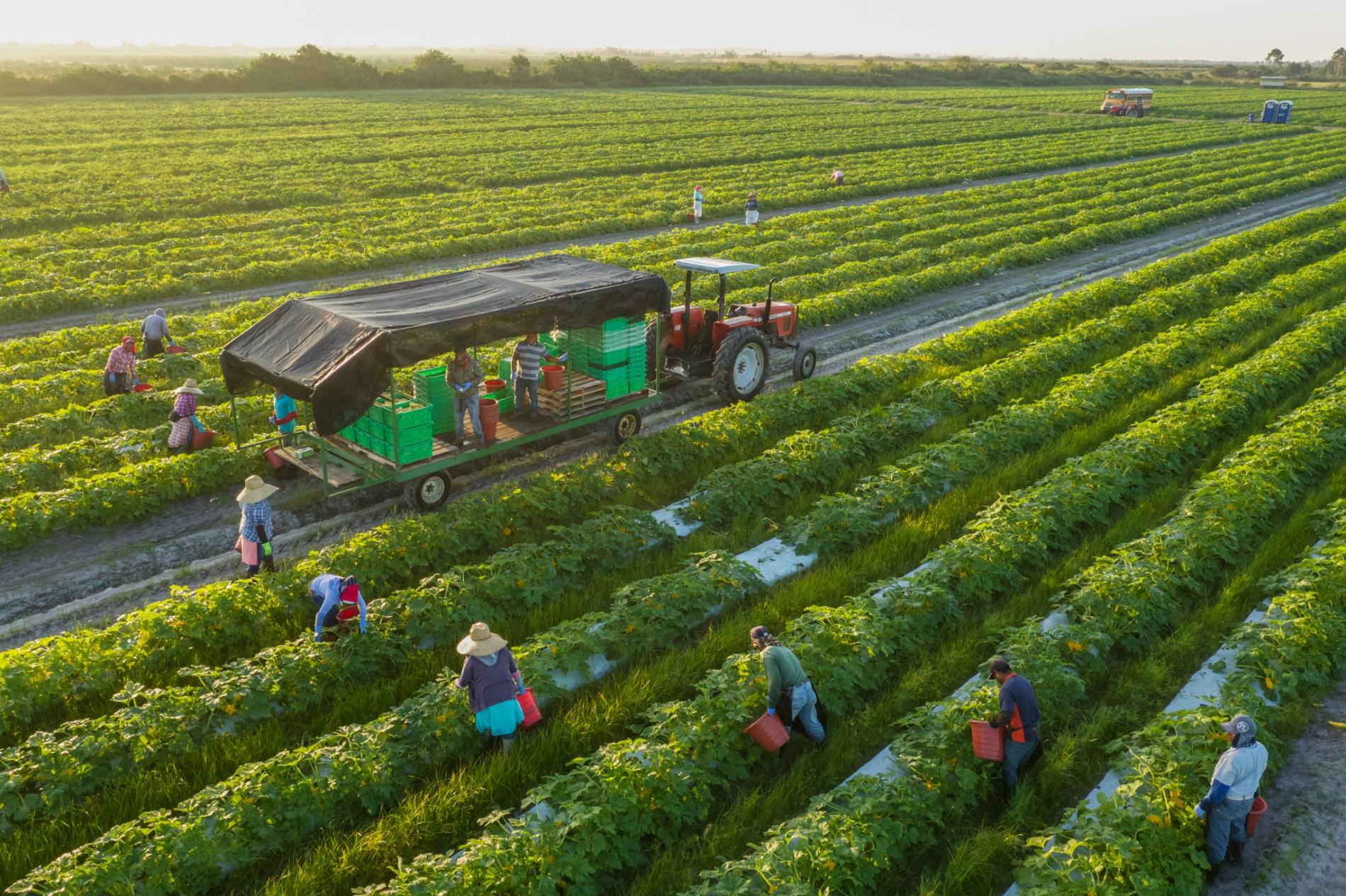
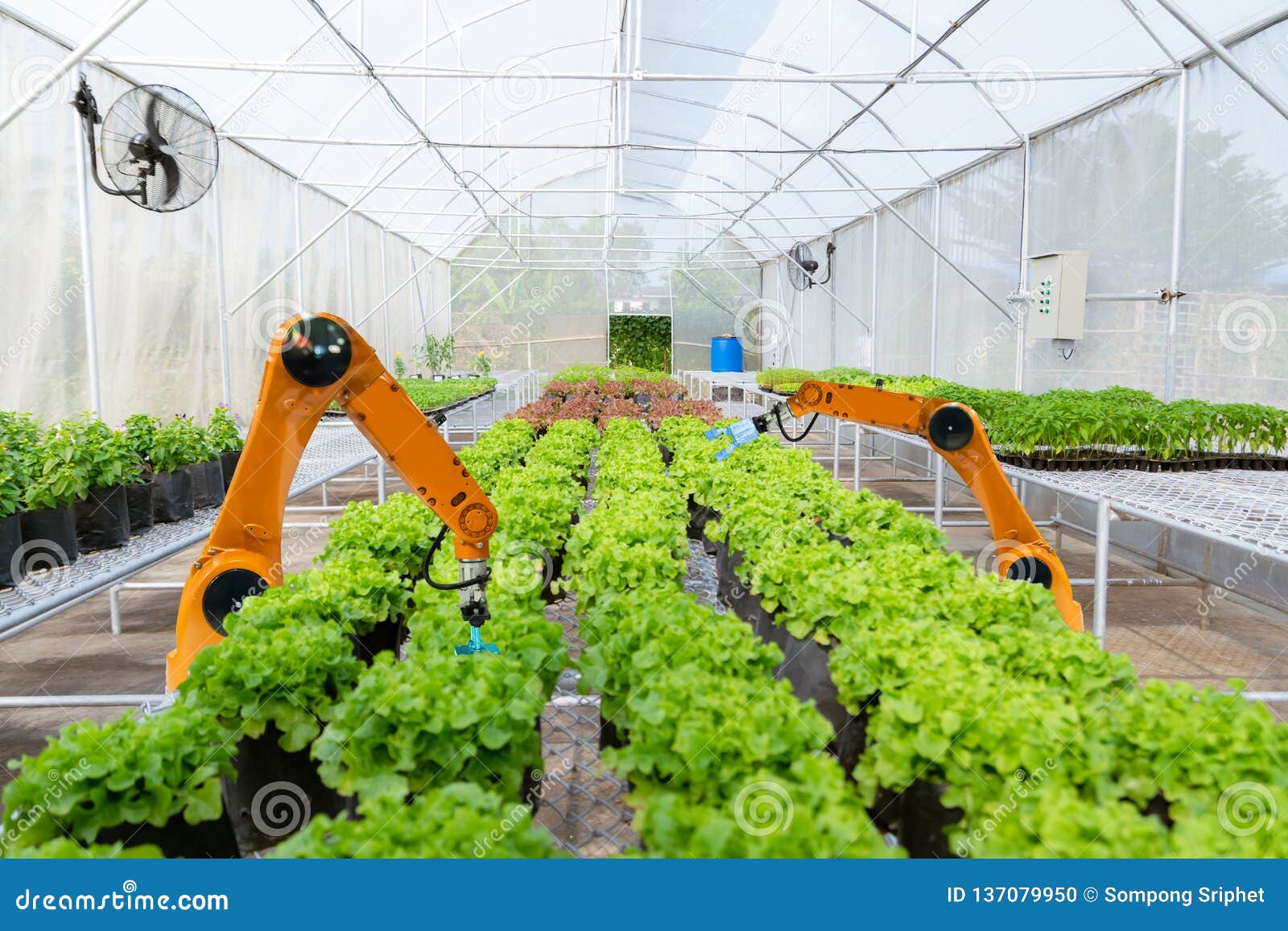
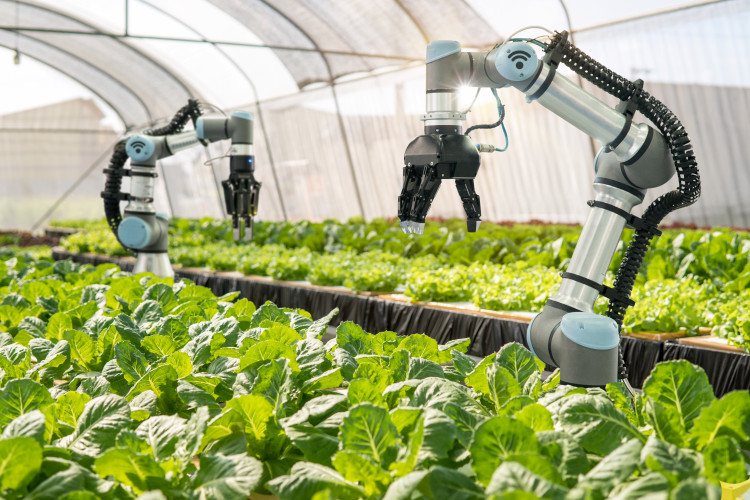
- Robotics and Automation: The rise of robotics is transforming farm labor. Startups like Abundant Robotics, Iron Ox, and Blue River Technology are developing robots that can perform tasks like picking fruits, weeding fields, and monitoring crop health. These innovations address labor shortages and improve efficiency.
- Data Analytics and AI: Platforms like Indigo Ag and Farmers Business Network are harnessing artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze data from various sources, providing farmers with insights into crop yields, market trends, and optimal farming practices.
Sustainable Agriculture:
Environmental sustainability is a major focus for many agricultural startups. They are developing solutions to reduce water usage, minimize chemical inputs, and promote biodiversity.
- Water Management: Startups like Pivot Irrigation and Watertronics are using sensors and smart irrigation systems to optimize water distribution, conserving precious resources and reducing water waste.
- Carbon Sequestration: Companies like Indigo and Kernza are exploring innovative ways to sequester carbon in the soil through regenerative farming practices and the development of climate-friendly crops.
- Alternative Protein Sources: The rise of plant-based and cultivated meat alternatives is disrupting the traditional food industry. Startups like Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat are creating plant-based burgers, sausages, and other products that mimic the taste and texture of meat, addressing concerns about animal welfare and environmental impact.
Direct-to-Consumer Revolution:
Technology is also empowering farmers to connect directly with consumers, bypassing traditional intermediaries and building stronger relationships with their customers.
- Farm-to-Table Platforms: Platforms like Farmigo, Local Roots, and Plenty are connecting consumers with local farmers, providing access to fresh, seasonal produce and supporting local food systems.
- Online Marketplaces: Websites and apps like Kickstarter and NeighborFood allow farmers to crowdfund their projects, pre-sell their products, and build communities around their farms.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the U.S. agricultural startup scene is vibrant, it faces several challenges:
- Funding: Securing funding can be difficult for early-stage agtech companies, as investors often require a clear path to profitability.
- Regulation: The agriculture sector is heavily regulated, and navigating these complexities can be a significant hurdle for startups.
- Adoption: Convincing farmers to adopt new technologies can be challenging due to resistance to change, lack of technical expertise, and the high cost of new equipment.
Despite these challenges, the future for U.S. agricultural startups is bright. The increasing demand for sustainable and technologically advanced solutions presents a significant opportunity for these innovators to make a real difference in the food system. As these startups continue to develop and scale, they have the potential to revolutionize how we produce, distribute, and consume food, creating a more efficient, equitable, and sustainable future.
Closure
We hope this article has uncovered key points about agricultural startups USA. Thank you for your attention to this article. See you again in our next article!.












.jpg)




