Sowing the Seeds of Change: Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture
With a focused perspective, we explore the engaging theme concerning Sowing the Seeds of Change: Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture. Our goal is to provide fascinating information and deliver a fresh outlook.
Video about Sowing the Seeds of Change: Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture
Sowing the Seeds of Change: Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture
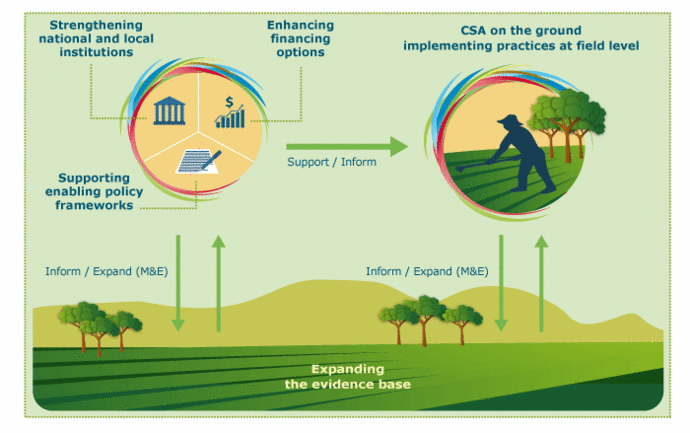
Climate change poses a significant threat to global food security, jeopardizing agricultural production and livelihoods worldwide. However, amidst the challenges, a beacon of hope emerges: climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This innovative approach aims to transform how we produce food, ensuring sustainability, resilience, and climate mitigation while safeguarding vital ecosystems.
Defining Climate-Smart Agriculture:
CSA is a holistic, integrated approach that combines three core objectives:
Sustainable intensification: Increasing agricultural productivity and yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Climate change adaptation: Strengthening agricultural systems’ ability to withstand and recover from climate-related shocks and stresses, such as droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures.
Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from agriculture and enhancing carbon sequestration in soils and ecosystems.
Unlocking the Potential of CSA:
CSA offers a multifaceted solution to the intertwined challenges of food security and climate change. Let’s delve into its diverse practices and benefits:
Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration: Healthy soil is the foundation of any thriving agricultural system. CSA emphasizes sustainable soil management practices like:
No-till farming: Minimizing soil disturbance reduces erosion and preserves soil structure, enhancing water infiltration and carbon storage.
Cover cropping: Planting non-cash crops during fallow periods protects soil from erosion, improves fertility, and increases organic matter content.
Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into farming systems provides numerous benefits, including soil stabilization, carbon sequestration, and diversification of income sources.
Closure
We hope this article has offered new perspectives on Sowing the Seeds of Change: Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture. We thank you for engaging with this content. See you in the next article!.

No comments:
Post a Comment