Investing in Integrity: A Look at Organic Farming Certification Costs
Today marks an exciting opportunity to explore the compelling subject concerning Investing in Integrity: A Look at Organic Farming Certification Costs. Let’s present insightful facts and deliver a new perspective to the readers.
Video about Investing in Integrity: A Look at Organic Farming Certification Costs
Investing in Integrity: A Look at Organic Farming Certification Costs
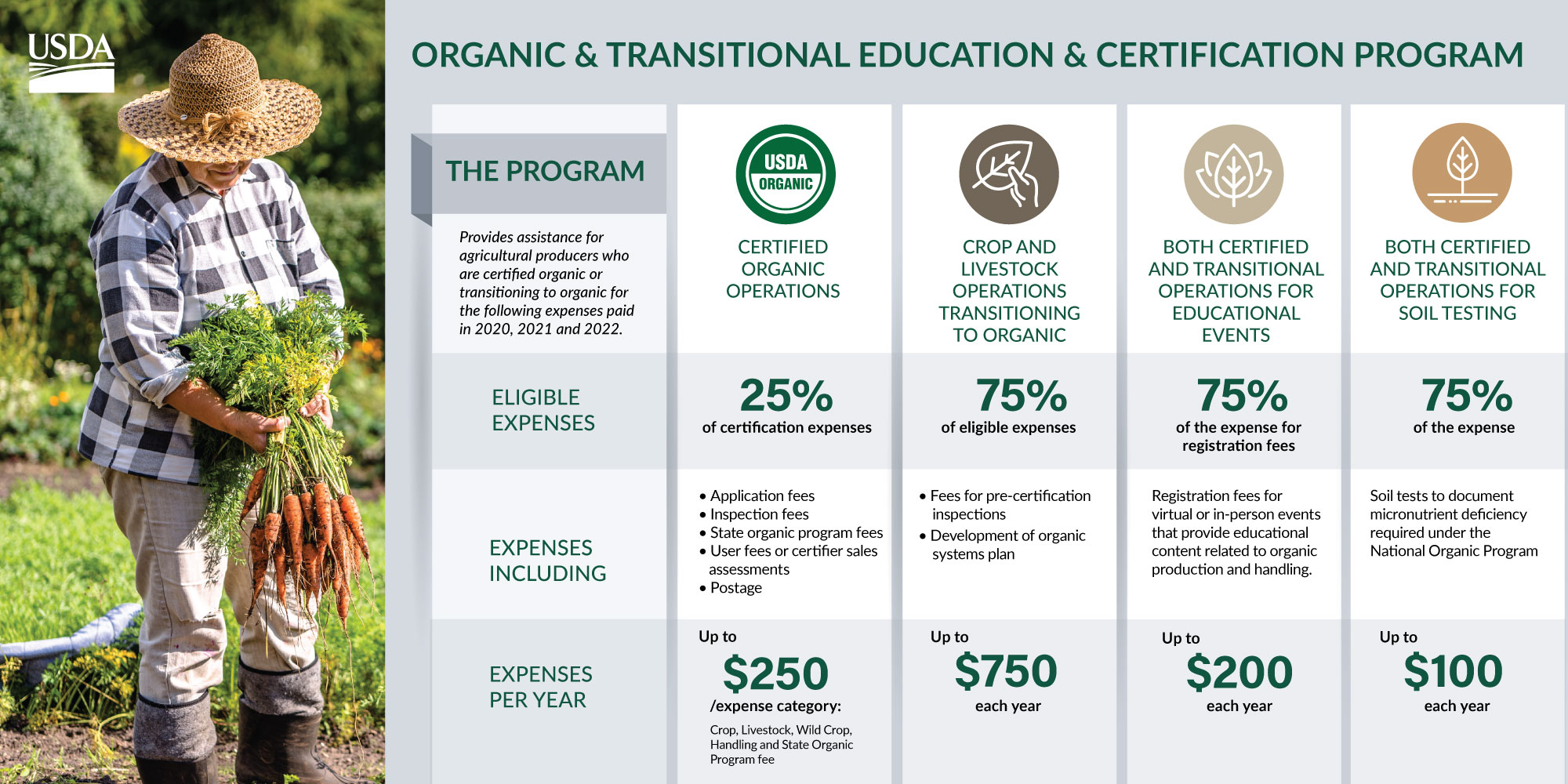
Organic farming, a system focused on sustainable agricultural practices and environmental stewardship, has witnessed a surge in popularity in recent years. Consumers are increasingly seeking food grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, driving demand for organically produced goods. However, the journey from conventional farming to certified organic requires a significant commitment, including navigating the costs associated with certification.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the financial implications of organic farming certification, exploring the various cost factors and providing insights into potential funding avenues.
Understanding the Certification Process:
Before diving into the costs, it’s crucial to understand the rigorous certification process. Organic certification ensures that farms adhere to strict standards set by accredited certifying bodies. These standards encompass various aspects, including:
- Prohibited Inputs: Substances like synthetic pesticides, herbicides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and prohibited antibiotics are banned in organic farming.
- Soil Health: Organic farms prioritize soil fertility through the use of organic amendments, cover crops, and crop rotations, minimizing reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
- Livestock Management: Organic livestock practices emphasize humane treatment, access to pasture, and organic feed, prohibiting certain growth hormones and antibiotics.
- Harvesting and Processing: Organic certification extends to handling, storage, and processing of produce, ensuring minimal contamination from non-organic materials.
Breaking Down the Costs:
The cost of organic certification varies significantly depending on several factors:
- Farm Size and Production Type: Larger farms or diverse production systems (e.g., crops and livestock) typically face higher certification costs due to the complexity of documentation and inspections.
- Certifying Body Fees: Different certifying bodies have varying fee structures, taking into account farm size, complexity, and geographic location.
- Inspector Costs: On-site inspections by accredited inspectors are essential for verifying compliance with organic standards. The frequency and duration of inspections influence the cost.
- Recordkeeping and Documentation: Organic farmers must maintain meticulous records of all agricultural practices, inputs, and farm operations. This record-keeping can involve software systems, labor costs, and potentially consulting fees.
- Transition Period Costs: Farms transitioning from conventional to organic may incur additional expenses related to soil amendments, pest control strategies, and livestock feed changes. This transition period often lasts several years.
Estimated Cost Range:
The estimated average cost of organic certification annually for a small to medium-sized farm can range from $500 to $2,500. Large-scale farms with complex operations may see costs exceeding $5,000 per year.
Financing Options for Certification:
The upfront costs of organic certification can be a barrier for many farmers, especially those starting their journey. Fortunately, several financing avenues exist:
- Government Programs: Certain government programs, such as the USDA Organic Certification Cost-Share Program, provide financial assistance to offset some of the certification costs.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Numerous non-profits offering grants and low-interest loans specifically to support organic farmers and their certification process.
- Private Lenders: Some banks and credit unions offer loans tailored for agricultural investments, including organic certification costs.
- Crowdfunding: Online crowdfunding platforms can be an innovative way for farmers to raise funds from individuals who support organic agriculture and their farm’s vision.
Closure
We trust this article has added valuable insights about Investing in Integrity: A Look at Organic Farming Certification Costs. We hope this article has been informative and useful. Until the next article!.

No comments:
Post a Comment